What affects a carbon score positively or negatively?

What is embodied carbon?
Embodied carbon or carbon content is measured in kilograms of CO2 equivalent per kilogram of product mass. If a carbon score is measured in tonnes that is fine, as long as the units are kept consistent. A carbon score is a measurement that can be used in every project to effectively work towards carbon neutrality.
Carbon scores are affected positively or negatively by the activity involved with the source materials and manufacturing processes.
A positive carbon score or carbon footprint is where the carbon emissions content registers more than zero. Being carbon positive contributes negatively to climate change.
A negatively affected carbon score is when the carbon content is reduced or carbon content is less than zero, which can be achieved where carbon is stored or sequestered.
To be carbon negative means that you're actively doing something positive for the climate. This is where the amount of CO₂ emissions removed from the atmosphere is more than the amount of CO₂ emissions released into the atmosphere. This impact is good.
Energy use and its impact on carbon scores
The amount of energy consumed during manufacture affects a carbon score up or down. For instance, recycling processes often use more energy to make a recycled material than the energy required initially for virgin materials.
The type of energy used to power manufacturing is a contributor to affecting carbon score up or down. Switching to renewable energy sources like solar or hydroelectricity help reduce the carbon score of a product which means that less offsetting is required to reach carbon neutrality in a project.
Choice of material and how it affects a carbon score
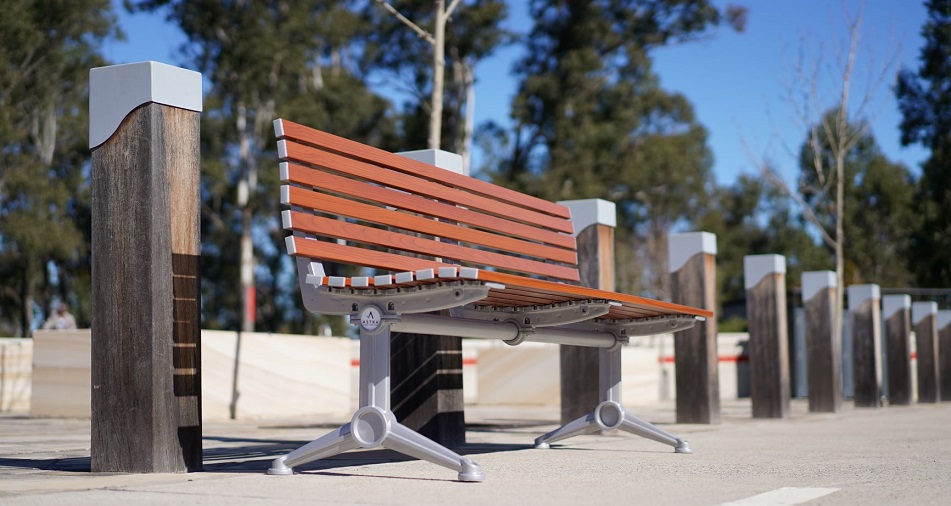
The weight of a material can also affect a carbon score positively or negatively. For example, steel has a 320 percent lower carbon content per kilogram compared to hydropower manufactured aluminium, but the mass for steel is 250 percent more dense which reduces the difference to a very similar score for the same item in aluminium.
Choice of material such as what type of slat on an outdoor seat or table will affect a carbon score up or down:
- Choosing timber over against aluminium can reduce the carbon score by two thirds by comparison.
- Choosing aluminium over against recycled composite material can reduce the carbon score by more than half by comparison.
- Choosing steel over against aluminium can reduce the carbon score by about two thirds by weight but only about 20% by volume.
How to reach carbon neutrality
A carbon offset is a reduction or removal of emissions of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases to compensate for carbon emissions made elsewhere. One tonne of carbon offset represents the reduction or removal of one tonne of carbon dioxide or its equivalent.
Carbon neutrality is achieved by balancing a measured amount of carbon released with an equivalent amount of carbon sequestered, avoided or offset.
Sequestration is the process of capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in a solid or liquid form to prevent atmospheric warming. Storage in solid form includes for example the carbon stored in timber over its lifetime which can be more than a hundred years in the case of timber framed buildings.
The natural process of photosynthesis in plants, where carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is converted to oxygen, also sequesters carbon into the soil. Forests convert the most CO2 to Oxygen during their peak growth stage which is from 10 to 30 years of age.
According to Timber NSW, well managed forests where trees are sustainably harvested in their early mature phase ensures that a forest’s carbon sequestration rate is kept at an optimal level. The more renewable forests that are sustainably harvested the better.


 Seating
Seating Benches
Benches  Curved Benches
Curved Benches Commercial Picnic Tables
Commercial Picnic Tables Concrete Plinth Mount Seating
Concrete Plinth Mount Seating Litter Bins
Litter Bins Bin Enclosures
Bin Enclosures  Shelters
Shelters Bike Parking
Bike Parking Architectural Bollards
Architectural Bollards Planter Boxes
Planter Boxes Skate Deterrents
Skate Deterrents  Drinking Fountains
Drinking Fountains Outdoor Classrooms
Outdoor Classrooms Athens Suite
Athens Suite Barcelona Suite
Barcelona Suite Berlin Suite
Berlin Suite Copenhagen Suite
Copenhagen Suite Dublin Suite
Dublin Suite Florence Suite
Florence Suite Glasgow Suite
Glasgow Suite Liverpool Suite
Liverpool Suite London Suite
London Suite Madrid Suite
Madrid Suite Manchester Suite
Manchester Suite  Milan Suite
Milan Suite Orbit Suite
Orbit Suite Paris Suite
Paris Suite Prague Suite
Prague Suite  Portsmouth Suite
Portsmouth Suite Rome Suite
Rome Suite Venice Suite
Venice Suite  Vienna Suite
Vienna Suite Woodville Suite
Woodville Suite School Furniture
School Furniture Healthcare Furniture
Healthcare Furniture Local Government Furniture
Local Government Furniture Park & Street Furniture
Park & Street Furniture Shopping Centre Furniture
Shopping Centre Furniture Aged Care Furniture
Aged Care Furniture